It may seem that ADHD is a disease primarily of children and young people. However, in approximately 65% of patients, ADHD symptoms persist into adulthood. This is not a big problem when ADHD is diagnosed and treated promptly.
Difficulties arise when the patient goes to the doctor only in adulthood. Unfortunately, adults with ADHD are often misdiagnosed and mistreated. Sometimes it happens that children were not diagnosed at all or were subjected to incorrect treatment for other diseases.
What is ADHD?
ADHD is a neurological disorder that causes inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. ADHD symptoms tend to decrease as people get older. The person typically becomes less hyperactive over time, but may still have difficulty concentrating and may be impulsive and risk-taking.
As a result, adults with ADHD have difficulty learning, working, and getting along with others. Adults with ADHD are also prone to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
Causes of ADHD in adults
Doctors are still not sure what causes ADHD.
However, there is growing evidence that genetics may play a role in the development of this condition. In addition to genetics, the following factors can increase the likelihood that a person will have ADHD:
- brain injury
- exposure to environmental factors such as lead during pregnancy or young adulthood
- alcohol and tobacco use during pregnancy
- low birth weight
- premature birth
There is currently no research to suggest that factors such as prolonged television viewing, high sugar consumption, or certain parenting practices cause ADHD. Although these factors can worsen symptoms, there is not enough evidence that they are the main causes of ADHD.
Tips for parents
The importance of the participation of a qualified specialist in the diagnosis and correction of attention deficit disorder is high, however, the main work falls on the shoulders of parents. The choice of parenting strategy determines whether a child will outgrow this disease or not. Recommendations to follow:
- take care of a balanced diet - include foods rich in protein, as well as iodine, zinc and magnesium in your diet, minimize the consumption of fast carbohydrates, you will notice how your child’s hyperactivity level will decrease;
- let your child “let off steam” - he will be more diligent during lessons;
- take into account the cyclical nature of the brain of children with ADD - they are not able to perceive information for longer than 7-10 minutes (and sometimes less), so “squeeze” the maximum out of your student at the beginning of the lesson, and not at the end, take breaks for physical activity more often;
- during classes, exclude all irritating factors to make it easier for him to concentrate on the main thing;
- do not set impossible tasks - give clear, short tasks, gradually increasing the level of difficulty;
- do not forget to praise your child even for the most minor achievements; self-esteem is his weak point;
- tell him words of love and support more often, try to spend more time together;
- establish a strict daily routine, teach order in the house from an early age - it is very important for children with ADD to be organized, this will simplify their adaptation in society;
- teach planning - this process is difficult for them;
- do not overload your child with activities; rest and healthy sleep are important elements in the process of restoring the nervous system;
- do not forget to rest yourself - rest will reduce stress and provide you with a surge of strength, vigor and positivity;
Do not be afraid of the diagnosis of “attention deficit disorder”; it does not mean that your child is developmentally delayed. He just needs a special approach to overcome the symptoms that prevent him from adapting to life and society. By paying due attention to this disease in childhood, your child has a great chance of outgrowing it.
ADHD in adults - symptoms
Some symptoms of ADHD in adults:
- the person is easily distracted and lacks attention, especially when bored
- does not listen to others, including interrupting and finishing sentences
- person has difficulty following instructions
- difficult to organize and complete activities
- he becomes restless and unable to sit still
- can be forgetful
- easily becomes irritable, impatient, or frustrated
- impulsive
How to help a child?
At present, attention deficit disorder cannot be cured. Speaking about the treatment of ADD, we are talking about methods of its correction, including medications, which significantly reduce the manifestation of key symptoms and make it possible to bring the child’s development closer to the age norm.
Drug treatment
To correct attention deficit disorder, different groups of drugs are used depending on the nature of the symptoms. Most often, therapy begins with psychostimulants, designed to stop pronounced features. Nootropic drugs are additionally prescribed to stimulate cerebral circulation. In cases of hyperexcitability, antipsychotic drugs are used.
When deciding on drug treatment, it is important to know the following:
- the drugs contain a number of side effects and contraindications, so they are prescribed to children in microdosages;
- psychostimulants should not be used in cases where ADD is accompanied by melancholy, low self-esteem, sleep and appetite disorders, as they can deepen the depressive state;
- the listed groups of medications do not belong to narcotic substances and do not cause addiction;
- It has been proven that the therapeutic effect of these drugs is observed only while taking them; after discontinuation of the course, the symptoms return again.
Only a doctor can prescribe medication. He will determine whether it is suitable for the patient, cancel it in time or select an alternative. Do not give drugs to your child at your own risk - this may aggravate his condition and cause adverse consequences.
Non-drug treatments
Depending on the clinical picture of the patient with ADD and his age, specialists prescribe non-drug methods of treatment or correction.
Physiotherapy and massage of the collar area - prescribed for children with birth injuries to the head and cervical spine. Massage, spinal gymnastics and physiotherapy (infrared heating) are prescribed after an examination, including an x-ray. The result is restoration of blood circulation in the cervical region, normalization of intracranial pressure.
Biofeedback therapy (biofeedback method) normalizes the bioelectrical activity of the brain, that is, the ability of its parts to send nerve impulses to neurons of all body systems. Such therapy eliminates the very cause of ADD.
Special sensors are attached to the child’s body, reflecting his biorhythms. Mental and physical activity causes them to fluctuate. The child is offered tasks, the correct completion of which triggers audio or visual reinforcement (a signal or a picture). The procedure is a success among children, while at the same time providing a powerful therapeutic effect.
Psychotherapy is designed to help a child accept his or her characteristics and adapt to the world and society around them. The specialist, through the game, shows the patient what behavior should be chosen in different situations: in a store, at school, on the playground or at home with parents. Additionally, exercises are practiced to increase concentration, perseverance, memory development, reduce impulsivity, etc.
Psychotherapy is one of the most effective ways to correct ADD; however, the positive effect is achieved over a long period - from 2 months or more.
Family therapy - during a conversation with parents, a specialist explains the features of the development and behavior of a child with attention deficit disorder, tells how you can and cannot influence him, gives advice on organizing classes and leisure time, selects games and teaching aids.
Art therapy : modeling, sand, drawing, playing musical instruments, breathing and meditative practices - all this is designed to reduce anxiety, develop perseverance and self-control, reveal talents and increase self-esteem.
ADHD in adults - diagnosis
Adults with ADHD are diagnosed based on criteria in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which describes the symptoms of mental illness.
Based on the symptoms, the doctor will decide which of the three types of ADHD the patient has. Three types of ADHD:
- ADHD combined type is the most common type of ADHD. The person exhibits impulsive and hyperactive behavior, is easily distracted, and has difficulty concentrating.
- ADHD impulsive/hyperactive type is the least common type. The person shows signs of hyperactivity and is constantly moving. He shows no signs of inattention.
- ADHD with inattention – People with this type of ADHD do not show signs of hyperactivity or impulsivity. Instead, the person is easily distracted and has difficulty concentrating. Basically, the “inattentive type” is the type that is often referred to as ADD because the term does not contain the word “hyperactivity.”
To be diagnosed with ADHD in an adult, the adult must have more than five of the following symptoms, lasting for 6 months.
Inattention
A person often:
- does not pay attention to detail or makes mistakes in work or other activities
- has difficulty paying attention to tasks and activities
- doesn't listen when people talk to him
- does not finish housework or workplace responsibilities
- have difficulty organizing events and tasks
- avoids or is reluctant to perform tasks that require mental effort for long periods of time
- loses things needed to complete tasks and activities
- easily distracted
- forgetful in daily activities
Hyperactive impulsivity
A person often:
- fidgets with legs or arms or cannot sit still
- gets up when he should be sitting
- gets restless
- can be very active
- talks a lot
- interrupts with questions
- has difficulty waiting his turn
- interrupts others
Other criteria
In addition to some of the above symptoms, there are:
- inattention or hyperactive-impulsive symptoms before age 12
- symptoms both at home and at work
- evidence that symptoms interfere with daily activities
- symptoms must not be the result of another mental health condition such as anxiety or depression
ADHD in adults - treatment
Drug treatment
Drug treatment usually consists of stimulants or non-stimulants. Stimulants increase the amount of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. These are two chemicals that improve attention and concentration.
However, stimulants may not be suitable for patients with high blood pressure, seizures, liver or kidney disease, or anxiety disorders.
Non-stimulants are slower but also improve concentration and attention and reduce impulsivity.
Some doctors may prescribe stimulants and non-stimulants to the same person to increase their effectiveness.
Psychotherapeutic therapy
Behavioral and cognitive behavioral therapy are aimed at helping the patient change their behavioral habits and teach methods of desired behavior. Doctors may also suggest joining a support group.
Accompanying illnesses
According to a 2020 article, there are several conditions that adults with ADHD may have.
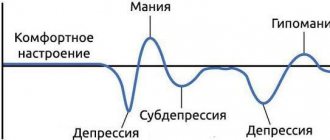
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder is a condition that causes people to be restless, talkative, and distracted. With this condition, there may also be periods of depressive and manic moods. Between 9.5% and 21.2% of patients with bipolar disorder also have ADHD, and between 5.1% and 47.1% of adults with ADHD have bipolar disorder.
Researchers suggest that having ADHD or bipolar disorder before age 18 increases the likelihood of developing the other condition over time.
Depression
Depression is another condition that typically coexists with ADHD. Some studies have shown that between 18.6% and 53.3% of adults with ADHD also suffer from depression. People who have both ADHD and depression self-report that their quality of life is lower than that of those who have only depression.
Anxiety disorder
Adults with ADHD are also more likely to suffer from anxiety than those without it. 50% of adults with ADHD have an anxiety disorder.
Adults with ADHD who have social phobia, such as fear of meeting or talking to people, are more common than adults with ADHD who experience panic disorder.
Substance use
According to a 2020 article, alcohol, nicotine, cannabis, and cocaine use are among the most common coexisting conditions with ADHD in adults. Some researchers suggest that substance use is twice as common in people with ADHD than in those without the condition. The most common type of substance use among adults with ADHD is cigarette use. People with ADHD tend to be more dependent on nicotine than those without ADHD.
Personality disorder
The same 2020 study reports that more than 50% of adults with ADHD have a personality disorder and that 25% of adults with ADHD have two or more personality disorders.
“They don’t need to be treated, they need to be educated”
Treatment and education are not mutually exclusive. When parents begin to understand the cause of the child’s problems and how to properly organize his life and studies, life becomes much easier for both the child and the parents. If you manage to find a common language with the school and organize help for the child at school, life almost completely returns to normal. It is possible to compensate for a lot, and with the right pedagogical approach, many children do without treatment. This, however, does not mean that no one needs treatment at all.