.
Since ancient times, such a state of the body as stress has been necessary to preserve life. He saved from death and gave the command to immediately mobilize all the strength and capabilities of the body. The benefit of stress was a quick reaction to danger. Rapid breathing, increased blood pressure, and the appearance of aggression. In this condition, all parts of the body are well supplied with blood, the brain makes quick decisions, the muscles tense and are able to perform many tasks that require endurance or quick movements. The strength for this is provided by glucose, adrenaline and cortisol, which, under the influence of stress, are released into the blood, provoke excitement and give a powerful impetus to action.
Stress - positive and negative aspects
Classification of stress: characteristics of the main types and stages of development
Nervous (psychological and emotional) stress is a set of nonspecific normal reactions of the body to physiological and psychological stress resulting from the influence of stressors (factors that cause stress) that upset the existing balance.
It can be caused by the influence of the external environment or internal experiences. It may also be due to general fatigue of the body and brain congestion.
The classification of types of nervous stress is carried out depending on the nature of the impact of the destabilizing factor, as well as on whether it has a positive effect on a person, stimulating his body to actively produce hormones, speed up metabolism, or simply kills nerve cells.
There are positive forms of stress (eustress) and negative ones (distress). According to the nature of the impact, stress is divided into neuropsychic, cold, thermal, light and others.
It is also necessary to characterize the two main types of stress - psychological and emotional.
Psychological is caused by social factors - these are worries about work, a change in activity or place of residence, problems with communication.
Emotional – the stimulating and calming abilities of the nervous system are disrupted due to internal processes occurring in the body.
Lack of sleep, poor nutrition and a disrupted daily routine affect not only the psyche, but also the functioning of nerve cells. It manifests itself in irritability, headaches and eating disorders (a person stops eating or, conversely, eats too much). This type of disease can only be treated with medications and the establishment of a clear sleep and nutrition regimen.
Among the main types of nervous stress, short-term (acute) and long-term (chronic) types are distinguished. These types manifest themselves in both positive and negative forms, as well as psychological and emotional ones. For example, there may be chronic psychological distress.
Stress is also characterized by the stages of its development, which were described back in 1936 by Hans Selye.
- Anxiety.
- Resistance.
- Exhaustion.
At first, a person is simply nervous, not noticing that his body is experiencing heavy psychological and emotional stress, then the symptoms appear more clearly, and the body begins to fight. During this period, outbursts of anger and sudden mood swings are possible. At the last stage, the person is apathetic and gets tired quickly. Depressive states are possible, you constantly want to sleep.
Cause of manifestation
In modern man, stress occurs due to an abundance of negative information. There is so much of it that the brain sometimes “freezes” like a computer. Anything that causes stress in a person is called stressors. Have you noticed how they work? A stressor initially causes anxiety. At this moment, the mobilization of protective forces occurs. Then comes a stage of resistance or equilibrium at a new elevated level. And further, if a person does not find a solution to an unfavorable situation, then he falls into a state of “exhaustion.”
The first stage occurs almost always. But what happens next—the second or third stage—depends on the mobilization of our internal moral, mental and physical strength. What it depends on and how the maximum protective reaction that weakens the effects of stress is achieved will be discussed in the next article.
For health: How to get out of depression on your own.
Positive and negative effects of stress on the modern human body
The mechanisms of stress and its effect on the human body have been studied in detail and are quite complex: they are associated with our hormonal, nervous, and vascular systems. What gives pleasure to one, makes another suffer. In addition, everyone's reaction to stress is different. One turns red, the second turns pale, the third eats non-stop, the fourth loses weight.
Everyone needs stress in small amounts. The positive effect of a little stress is that it makes you think, look for a way out of the situation, and motivates you to solve the problem. In addition, the positive effect of overexcitation on the body includes acceleration of the functioning of all organs and systems (for example, acceleration of metabolism, blood circulation and the release of hormones that help regulate nervous tension).
But the life of a modern person is oversaturated with stress, which accumulates in the body and manifests itself in a number of adverse consequences. The negative effects of severe stress can be very different for certain people, but here are just a few of the results that are most often manifested in the majority of patients who have suffered a nervous shock.
For example, a psychological or emotional shock experienced by the body can result in a weakening of the immune system, as well as the gastrointestinal tract, heart, blood vessels and endocrine system. This can lead to diseases such as angina pectoris, hypertension, heart attack, gastritis, ulcers, colitis, cholelithiasis, insomnia, and diabetes.
How stress affects your body
To give you a quick overview, when you experience acute stress—whether it's real or imagined because your body can't tell the difference—your body releases stress hormones (like cortisol) that prepare it to fight or flee the stressful event.
Your heart rate increases, your lungs take in more oxygen, your blood flow increases, and parts of your immune system are temporarily suppressed, reducing the inflammatory response to pathogens and other foreign invaders.
When stress becomes chronic, your immune system becomes increasingly resistant to cortisol, and since inflammation is partially regulated by this hormone, this decreased sensitivity increases the inflammatory response and allows inflammation to get out of control. 3
Inflammation, in turn, is a hallmark of most diseases, from diabetes to heart disease and cancer. Elevated cortisol levels also affect your memory, causing a gradual loss of synapses in the prefrontal cortex. 4
Stress can even trigger the development of dementia. In one study, 5 72 percent—nearly three out of four—of patients with Alzheimer's disease experienced severe emotional distress in the two years preceding their diagnosis.
The influence of constant stress on the nervous system and its consequences for the body
The effect of severe stress on the nervous system can cause neuroses, depression and apathy. During a shock, a person loses a lot of nerve cells, the brain works in increased mode, and the endocrine glands produce excessive amounts of hormones that regulate psychological stress (glucocorticoids).
Accordingly, when the body has managed to relieve stress and overcome the disease, it goes into saving mode. Due to the subsequent economical production of endorphin and oxytocin, the consequence of the stress experienced for the body is isolation, apathy, and irritability.
In such cases, doctors recommend eating as many foods as possible that stimulate the production of “joy hormones” (hard cheese, liver, dark chocolate), as well as spending as much time as possible with loved ones and in the fresh air.
The impact of stress on a person's health can also affect the musculoskeletal system. For example, due to the fact that during stress the body produces an excessive amount of glucocorticoids, which do not have time to be absorbed. After the tension is relieved, they seem to “wander” throughout the body, bringing only harm to it - they contribute to the breakdown of nucleic acids, thereby weakening the muscles and causing the risk of dystrophy.
Osteoporosis can also be a consequence of constant (chronic) stress. Those same “unused” glucocorticoids interfere with the absorption of calcium. This leads to thinning of the bone tissue. This disease is especially common among women.
May have stress and effects on the skin, such as inhibiting the renewal of fibroblasts (connective tissue cells). This leads to the fact that the skin becomes sensitive to irritants, small wounds heal worse on it and acne and inflammation appear more often.
Eustress is a form of stress that does not harm the body.
Eustress is a form of stress that does not harm the body.
Eustress is a condition that helps to increase the functional reserve of the body and adapt to a stress factor. It helps to cope with difficult life situations and develop physical and emotional endurance. Overcoming difficulties causes a pleasant feeling of euphoria and positive emotions, which allows you to forget about the experiences you had to endure. Thus, eustress is necessary for normal functioning.
Causes of Eustress
The following reasons are identified for the development of a positive stress state, as well as its preservation without transition to a negative form - distress:
- the presence of a difficult situation for a person that contributes to an increase in the level of adrenaline in the blood;
- a sharp surge of bright positive emotions;
- minimal experience of confronting factors that provoke stress;
- awareness of positive reactions or support from others;
- the physical ability of the body to cope with the obstacle that has arisen.
Types of stressors
Stress factors affect the body in almost any environment. Stress occurs very often, and this is normal. In healthy people, it performs adaptive and protective functions. Stressors can be:
· negative environmental factors (unfavorable climate, air pollution, high levels of radiation);
· disruption of physiological processes due to various health problems;
· work with a high risk to life, in extreme conditions;
· the need for accelerated information processing (time shortage);
· perceived threat to life associated with any reasons;
· group pressure or ostracism (ignoring, non-acceptance);
· isolation (eg imprisonment);
· inability to control events occurring in life;
· deprivation of sleep, communication;
· lack of life purpose.
What happens in the body during eustress
Stress is a biological mechanism associated with the release of hormones into the blood. When the cerebral cortex perceives a situation as threatening, excitation passes through a chain of neurons to the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Pituitary cells produce adrenocorticotropic hormone, as a result of which the adrenal cortex is activated. They produce and release stress hormones – cortisol and adrenaline – into the blood.
Positive effects of eustress
A surge of vigor. As a result of the influence of stress hormones, metabolism accelerates: proteins are broken down into amino acids, glucose levels in the blood increase - cells are provided with additional energy. As a result, a person feels cheerful, even if he was previously tired.
Stimulation of intellectual abilities. Under the influence of hormones, breathing becomes more frequent, and as a result, blood supply to the brain improves. This leads to improved cognitive functions. In a state of eustress, a person can quickly come to a solution to a complex problem.
Increased muscle strength. Due to this physiological mechanism, the body temporarily becomes stronger and more resilient. Increasing muscle tone allows you to implement the “fight or flight” scenario.
Reduce possible bleeding. When stressed, the number of platelets in the blood increases. By increasing clotting, if a person is injured, the risk of major blood loss is reduced.
Reduced activity of secondary body functions. The body saves energy, freeing up resources to combat stress, by reducing the formation of immune cells, reducing intestinal motility, and suppressing the work of the endocrine glands.
Reducing the risk of allergic reactions. The stress hormone cortisol has a depressing effect on the immune system. This reduces the likelihood of developing allergies, which are essentially a reaction of the immune system to certain factors.
Eustress mobilizes and forces you to gather strength to find a way out of a difficult situation. This also enriches life experience: in the future, being in the same conditions, a person will feel more confident. Eustress increases adaptive abilities and can have a beneficial effect on personality development. However, it is important that the difficult situation is successfully resolved before the body's resources are exhausted.
Diagnosis of eustress
There are methods for objectively assessing the degree of stress development. First of all, these are laboratory tests to determine the level of hormones in the blood: adrenaline, norepinephrine, cortisol and cortisone. The higher their concentration in the blood, the more pronounced the stress reactions. Their intensity can also be assessed using the electromyography method (registration of bioelectric impulses in the muscles).
How does eustress differ from distress?
Type of reaction. Eustress is an adaptive, protective reaction to the influence of negative factors. It activates and mobilizes the body's internal reserves and can temporarily improve some physiological functions. Distress is a pathological reaction. It disorganizes human behavior and negatively affects health.
Duration of action. Eustress is usually short-term, accompanied by rapid consumption of part of the adaptive reserves at the surface level. Distress is usually long-lasting and can develop into mental pathologies or cause somatic disorders.
Need for treatment. Eustress usually goes away on its own without consequences. Treatment is required only in a situation where the body cannot cope with such a load. Distress necessarily requires correction, as it can lead to physical and mental disorders.
Consequences of the transition from eustress to distress
With prolonged exposure to a stress factor, the hormones adrenaline and cortisol begin to negatively affect the body's functions, vasospasm occurs and the nervous system becomes overworked. Possible consequences include:
- decreased concentration and memory impairment;
- fussiness, lack of concentration, due to which a person can make rash decisions;
- increased fatigue and low performance as a result of disruption of neural connections in the cerebral cortex;
- increased risk of developing depression, development of general dissatisfaction with life, partner, work, etc.;
- problems in family and sexual life;
- decreased self-esteem;
- increased irritability and aggressiveness, which complicates social interaction and delays the resolution of conflict situations;
- the desire to relieve psycho-emotional stress by consuming alcohol or drugs;
- loss of control over thoughts and emotions (nervous breakdown).
Prevention of the transition of eustress to distress
In relation to stress, the position of the person himself and his responsible approach to maintaining health are important. The following measures can help avoid the transition of the body's adaptive reaction to a destructive state:
1. Therapeutic training - it is important that a person understands the nature of stress and can find out the reasons underlying this condition.
2. Balanced nutrition - during periods of increased psycho-emotional stress, it is recommended to avoid foods and drinks that stimulate the central nervous system, such as coffee.
3. Using various relaxation techniques - it is possible to use muscle and psychological relaxation, and perform breathing exercises (if there are no contraindications).
4. Physical activity - during periods of stress, any type of activity performed in the fresh air without competition (walking, jogging) can help.
Corvalol PHYTO1 for stress
Corvalol PHYTO is a herbal preparation that has a complex effect due to its multicomponent composition. The product contains peppermint oil, ethyl bromizovalerate and motherwort extract. Corvalol PHYTO can be used as part of complex stress therapy to correct neurosis-like conditions, sleep disorders, tachycardia, states of excitation (with pronounced vegetative manifestations), intestinal spasms2. The drug is available in two dosage forms: drops and tablets.
___________
1 Has contraindications. Before using the drug, consultation with a specialist is necessary. 2 Instructions for use of the medicinal product for medical use Corvalol PHYTO (tablets, drops).
The main signs of stress and the human body’s reaction to common symptoms
The main signs and common symptoms of stress: the appearance of pain in the head and neck, heart, and abdomen; increased blood pressure; feeling of a “lump in the throat”, shortness of breath, “choking” of the voice; sleep disturbance, depression, physical weakness, headache, fatigue, reluctance to do anything, decreased concentration, memory problems and decreased thinking speed, making it difficult to study or work.
Also, a symptom and reaction of the body to stress may be a lack of interest in others, even in best friends, in family and friends; Nervous tics and obsessive habits often appear: lip biting, nail biting, etc.; constant feeling of guilt, nervousness, anxiety; inadequate reaction to minor troubles; loss of appetite - from its absence to an increased feeling of hunger; sexual disorders.
The reaction of a sick person’s body to stress may be delayed. It is a repeated reaction of the body to a strong nervous shock (the death of a loved one, a disaster experienced).
It appears several weeks or months after the shock (from 2 weeks to six months). At the same time, a person may have dreams about the experience, fall into numbness, and be tormented by constant memories and even a substitution of reality. Such a patient most often avoids actions that may evoke memories of an unpleasant event.
In this case, drug treatment and consultation with a psychotherapist are necessary.
Signs of severe stress
Stress protects a person from a strong irritant and neutralizes possible negative consequences. The body’s reactions vary, but everyone has symptoms of a kind of burnout. The physical and psychological spheres suffer. Signs of an unstable stress state appear quickly.
It is important that at this stage there is someone close to the person. Many symptoms of severe stress appear for the first time and are often noticed only by people who know the person's character intimately. Not everyone knows what to do in such cases.
A person has impaired memory, concentration, thoughts are focused on negative events, and from the whole series of news they unconsciously choose exclusively negative ones. Emotional symptoms include increased irritability, which gradually increases, leading to a state of despondency and prolonged depression. Difficult experiences can turn into an acute feeling of loneliness with detachment from the surrounding reality and isolation.
Symptoms of stress can be:
Physical signs include periodic nausea that has no reason, impaired digestion of food in the form of constipation or diarrhea, and decreased libido. Severe dizziness and increased heart rate are possible. Signs of severe stress in women are increased emotionality, irritability, tearfulness, and menstrual irregularities.
For a man, stress occurs differently. Although the male body is strong emotionally, exacerbation of chronic diseases may occur, disturbances in the functioning of the heart and genital organs may appear as a consequence of emotional experiences.
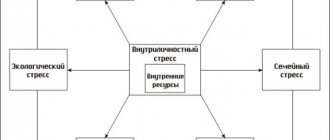
Causes of different types of stress
The causes of stress are divided into two types:
- Mental-emotional.
- Physical.
The first cause of nervous tension is common to all mammals. Change of habitat, activity, weather - any changes in the environment affect the human psyche. If the brain does not have time to cope with a large amount of information coming from the outside, the body experiences emotional and psychological stress, which affects not only the nervous system, but also all organs.
Physical reasons that most often cause stress can be an infection that has entered the body, changes in diet and sleep patterns. In this case, the glands that secrete hormones into the blood - the adrenal glands, the pituitary gland and the thyroid gland - begin to work worse, and this leads to a lack of hormones that regulate the body's rest processes, an excess of adrenaline and poor absorption of iodine.
The causes of nervous stress can also be “mixed”: when bad weather is combined with a cold and problems at work. In this case, to effectively combat tension, you need to “fight on all fronts” and eliminate all irritants that depend on you. So, for example, you can’t do anything about weather conditions, but you can solve problems at work and fight infection.
Stress factors influencing its development
Factors influencing the development of stress in a person can be divided into two main groups: work and personal.
Operating factors:
- Poor relationships with colleagues.
- Insufficient load.
- Excessive load.
- Lack of career growth.
- Harsh physical working conditions.
- Perform multiple tasks simultaneously.
The interaction of several of these factors, constant fatigue and dissatisfaction with one’s job, salary level and humiliation from superiors and colleagues lead not only to stress at work, but also cause the risk of nervous breakdowns, depression and neuroses.
Personal factors causing severe stress are as follows:
- Poor health.
- Quarrels and problems in the family.
- Low or high self-esteem.
- Environmental change.
- Poor nutrition.
- Changing your sleep pattern.
Most often, nervous tension occurs when factors from both groups interact.
Stress concept
You and I know well what a state of stress is. Whether we like it or not, we face it every day, constantly. This condition is chronic. Throughout our lives, we are forced to adapt to or overcome various environmental factors.
Portrait of tired young Asian business woman feeling stress from work. Stress at work and emotional pressure concept.
The best defense against stress is adaptation to unfamiliar situations in life. In general, adaptation, from Latin, means adaptation. The body somehow needs to survive, and it adapts to the changed conditions of existence. He needs “immunity”. So he develops, with the help of adaptation, some resistance to unwanted events or actions. This process is considered stress.
Those. stress acts as a certain defense of the body from something.
How to quickly relieve nervous stress at home: effective methods of combating it
It is important to be able to recognize the onset of stress, find out its causes and signs (work or home tension, apathy, headaches and neuroses). Depending on what causes nervous tension, it is necessary to remove the irritant (if possible), deal with external symptoms and put the nervous system in order.
The disease cannot be allowed to develop to an uncontrolled level. A person may not realize that he is under stress, he may get used to it and not notice it at all. But even in this form, it weakens the body and deprives a person of many opportunities.
In order to understand how to quickly relieve nervous stress at home, you need to answer three main questions for yourself:
- What is the cause of stress?
- How can the cause be eliminated?
- How can you relax and calm down?
Remember that the first step to solving a problem is accepting it. If you accept the fact that your psyche is in serious danger, that this is not just overwork, but a severe shock to your body, it will be easier for you to solve this problem.
First, find the stress-forming factor. Remember that there may be several of them. And the problem should be looked for both at work and in the family. Next, try to eliminate or accept it.
An effective method of dealing with severe stress at the second stage is to “exhale anxiety”: inhale slowly and deeply through your nose, then exhale all your worries through your mouth into an imaginary ball. After each exhalation, you need to imagine how the ball increases in size. When the balloon is inflated, you need to release it. He will fly away and take all worries with him.
You may need psychological auto-training under the guidance of a doctor. A specialist will help you figure out what to do with the problem: solve it or accept it, and will also monitor the entire recovery process.
The third stage is relaxation and calm. It can be described as the main treatment and development of stress resistance in the body.
Stress as a factor in polycystic ovary syndrome
As noted in a recent article by Chris Kresser,6 stress may also be a factor in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition caused by elevated levels of androgens, which are male sex hormones that can affect a woman's menstrual cycle, fertility, weight, and more.
This may be especially true if you:
- Undereat and overtrain to improve your physique
- No cystic ovaries
- Your weight is normal or below normal and you do not struggle with insulin resistance.
The article goes into much more detail about the hormonal cascade that can ultimately lead to PCOS, but in general, stress causes your body to produce a number of hormones, starting with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal glands to produce stress hormones. such as cortisol and adrenaline.
Currently reading: Chemotherapy and radiation should be banned!
ACTH also triggers the production of adrenal androgen hormones, including androstenedione, which is one of the two main androgen hormones that cause symptoms of PCOS in women.
Treatments for nervous stress and prevention techniques
Treatment and subsequent prevention of stress can be carried out by two main methods: medication and non-drug.
Non-drug treatment. It has been established that most physical diseases are the consequences of chronic stress, so you need to learn to manage stress: isolate yourself from the stressor or change your attitude towards it; try to get more positive emotions. Communication with nature, short walks, and listening to music are also important.
Non-drug ways to combat any stress include dietary nutrition.
It involves giving up heavy food (so that it is easier for the body to absorb it and it does not waste extra energy on digestion). For example, you should exclude fried meat, legumes, lard, fatty confectionery and milk chocolate from your diet. It is necessary to minimize the consumption of potatoes, bread, and red meat.
Answering the question of how to relieve nervous stress with proper nutrition at home, psychotherapists recommend eating mostly raw food: fruits and vegetables. Also allowed are porridges (buckwheat and pearl barley, rich in vitamins and microelements), dairy and fermented milk products, dark chocolate and boiled chicken. You won’t even notice how you will start to feel better.
Drug treatment of the disease nervous stress involves taking the Antistress , consisting of four products – “Hyper” (antidepressant), “Mystic” (relieves insomnia), “Revien” (eliminates anxiety) and “Passilat” (eliminates stress) .
Most of these drugs are sold by prescription only, so consultation with a doctor is necessary.
In addition, treating nervous stress with antidepressants alone relieves symptoms, but does not completely solve the problem. Drugs such as Imipramine or Befol may cause drowsiness and irritability. But it is precisely these problems that a person tries to fight under stress.
That is why it is necessary for your doctor to select a group of medications for you in addition to antidepressants.
The fight against nervous tension does not end once you feel better and calmer.
How can you restore your nervous system after prolonged stress and methods of prevention?
Answering the question of how the nervous system can be restored after prolonged (chronic) stress, experts agree that the patient needs a change of environment. Move away from the irritant, relax at the seaside or in the mountains, quit a job that is burdensome, try to live separately from your spouse in order to sort out your feelings (if the stress is caused by family quarrels).
=Drug treatment should not be continued without the appropriate instructions from a doctor. If a specialist sees that you should take the course again, he will prescribe weaker analogues of drugs so that your body does not get used to sleeping pills and antidepressants.
No one thinks about the need to take care of their nervous system until they are faced with serious problems. Preventing stress often helps to avoid unpleasant overstimulation of the psyche, and also, if a shock does occur, to cope with it faster.
Psychologists identify the following methods for preventing nervous stress:
- It's easier to deal with problems.
- Learn positive thinking
- Switch from thoughts about problems.
- Learn to throw out negative emotions.
- Learn to relax.
- To walk alot.
- Do yoga.
- Take a bath with sea salt.
- Keep a diary.
- Learn to speak frankly with loved ones.
If everything is clear about walking, baths and yoga, then the remaining points require more detailed consideration.
Taking a more relaxed approach to problems and being able to switch essentially means learning to divide your problems into big and small, as well as those that need to be solved now and those that can wait. Psychologists also advise not to “carry” work problems home and vice versa.
Another good technique for preventing nervous tension and stress is positive thinking. Pessimists have a much harder time coping with even the most insignificant problems than those who, when taking on a decision, expect a positive result.
You can throw out negative emotions through sports. For example, boxing or fencing would be suitable. Some psychologists advise moving away from people and shouting. Forest, field - you will only scare away the birds.
Learning to relax is actually not as easy as many people think. It is important to be able to relax without TV/Internet and alcohol. Lie down, close your eyes and immerse yourself in your thoughts, relax every muscle. Half an hour of such relaxation a day will help you avoid nervous breakdowns.
Another effective way to prevent severe stress is to talk about the events of the day and accumulated problems. You can talk to your loved ones or keep a diary. But there are several rules for such conversations.
When talking to loved ones:
- Be completely honest.
- If the topic is unpleasant to you, switch.
- Know how to listen.
- Take criticism appropriately.
- Don't think that the other person is dumber than you.
- Spend at least half an hour a day talking.
When a person discusses something with a friend or family, he has the opportunity not only to solve the problem at the stage of its development, but also to receive warmth and support. It is also important to hug those you care about to feel needed and protected.
When you keep a diary, don’t write dryly—let it be your “stream of consciousness.” In addition, do not try to solve the problem on the pages of a notebook - you just need to understand it and think about ways to solve it.
Don’t hold back your emotions - if you were offended, first express all your feelings, and then try to figure out why the person did this, and thank him in the pages of your diary for the experience he gave you.
Breathwork can reduce stress and help you develop greater resilience
There are many breathing techniques, almost all of which can help you get in touch with your body and calm your mind. One of my personal favorites is the 4-7-8 breathing exercise taught by Dr. Andrew Weil 10, who recommends using it “whenever something unpleasant happens—before you react” and “whenever you feel inner tension.”
The key to this exercise is to remember the numbers 4, 7 and 8. It is important not to focus on how much time you spend on each phase of breathing activity, but rather on the correct ratio.
You can do this exercise as often as you like throughout the day, but it is recommended not to take more than four full breaths for the first month or so of practice. Later, you can work up to eight full breaths at a time. If you do this, I think you will be pleasantly surprised at how quickly and easily it can center and relax you. Here's how it's done:
- Sit up straight and place the tip of your tongue against the back of your front teeth. Keep it there throughout the breathing process
- Inhale quietly through your nose for a count of 4.
- Hold your breath until the count of 7
- Exhale through your mouth for a count of 8, making a distinct whooshing sound. This completes one full breath
- Repeat the cycle three more times, for a total of 4 breaths (after the first month, you can work up to 8 breaths per session).
Causes, main symptoms and signs of stress in children
Signs of nervous stress are more difficult to recognize in children than in adults. Until the age of 10, the child himself often does not realize that he is in a state of nervous shock. Between the ages of 12 and 15, children already understand their emotional state, but rarely share their own problems with their parents. Puberty is characterized by irritability, laziness, lack of interest in family affairs and new (often incomprehensible to adults) hobbies. Therefore, mothers often mistake the characteristics of adolescence for a stressful condition.
The main symptoms of stress in a young child (up to 8-10 years old) are:
- Demanding and indignation.
- Increased fears.
- Manifestation of speech defects.
- Fatigue.
- Closedness, reluctance to go for walks.
- Memory impairment.
- Decreased appetite.
Of course, if you notice one or more signs in your baby, then you should not immediately panic and run to a psychotherapist. If there is no obvious reason that could cause anxiety (a move, a change of team, a quarrel in the family, a shock or a long-term illness), then most likely the child just wants to attract your attention or change something in his daily routine.
Stress in children 12-15 manifests itself in the same way as in adults - apathy, irritability, and reluctance to talk about problems. But in adolescents these signs are much more pronounced.
If the child is simply gloomy and unfriendly, most likely these are the hardships of adolescence, but if he constantly cries, snaps and locks himself in the room, you should seek help from a psychologist or try to independently contact your child and help him solve the problem.
The main causes of nervous stress in children during adolescence are:
- Change of team.
- Failures in relationships with the opposite sex.
- Low performance at school.
- Quarrels with parents.
- Parental prohibitions.
- Failures in finding a hobby and creative fulfillment.
- Past illness.
- Dissatisfaction with the changes that are happening to their body.
Of course, at this age a child may experience displeasure even from the slightest changes in life, but this cannot be called stress.
The impact of stress on a child and its consequences
The impact of stress on a child is the same as on an adult. The nervous, endocrine, and cardiovascular systems may suffer. It is especially important to pay attention to the fact that glucocorticoids, which are released during stress, negatively affect the absorption of calcium in the bones and can lead to muscle dystrophy.
For children and adolescents, this problem is especially dangerous, since their musculoskeletal system is weaker than that of an adult.
In this case, it is necessary to strengthen the child’s bones with the help of vitamin complexes (for example, Calcimin or Omega 3 ), and develop muscles with a large amount of protein in the diet.
A consequence of stress experienced in children is also often intercostal neuralgia - inflammation of the nerve between the ribs. Characterized by severe, sometimes “wandering” pain in the chest or back. Massages (a course can only be prescribed by a neurologist), as well as painkillers ( No-Spa , Ibuprofen ), will help you cope with neuralgia.
Stress and man
The very effect of stress on humans is constantly being studied. The creator of the theory of stress, the famous Canadian biologist Hans Selye, compares stress with a certain nonspecific response of the body to any demand presented to it. Selye claims that life without stress is impossible.
We cannot live without stress, because then any tension is eliminated, and complete freedom sets in, which leads a person to a state of “amoebism”. After all, when we experience discomfort in something, we try to overcome what we don’t like. We think, plan, look for ways, act to eliminate the influence of this “inconvenience” on our lives.
When we disagree with the problems that stress presents to us, we find their solution, i.e. somehow we move and do something to overcome these problems. Selye wrote that life without stress means death, that “stress is not just life, it is the aroma and taste of life.”
I conclude that stress is the engine of our lives, so that we do not become sour and bored.