Medical information is reliable Checked by Eremin Alexey Valentinovich
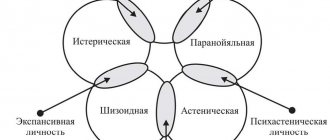
Emotionally unstable personality disorder (ENPD) is a mental disorder in which a person is impulsive, has poor self-control, and is unbalanced in words and actions. The condition requires the appointment of long-term psychotherapy, in which a specialist determines the causes of the development of the pathology and corrects them.
The psychiatric department of Dr. Isaev’s clinic offers treatment for emotionally unstable personality disorder in Moscow. Here, a thorough diagnosis is practiced, based on the results of which an individual correction program is drawn up. The therapeutic course includes traditional methods of psychotherapy and innovative proprietary techniques. Pharmacology is used if necessary. The result is a stable state of remission, normalization of mental processes and the emotional sphere.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The incidence of ENRL in the population is 2-4%. It is predominantly detected in women. The clear reason for the development of the pathology is unknown. However, in many patients a hereditary predisposition is clearly identified.
Risk factors for the development of pathology include:
- Organic disorders in the brain: consequences of traumatic brain injuries, malignant neoplasms and other lesions.
- Minimal brain dysfunction occurring in childhood. The condition is characterized by a temporary disruption of the blood supply to the structures of the central nervous system.
- Negative emotional atmosphere in the family, including aggressiveness or cruelty of parents, authoritarian parenting style, demand for total obedience from children.
- Lack of parental attention and affection in childhood.
As a rule, several risk factors are identified in patients with emotionally unstable personality disorder.
Instability or instability
Emotional instability is a state opposite to psycho-emotional stability.
A psycho-emotionally unstable person reacts inadequately to stimuli, it is more difficult for him to concentrate, and any, even minor, trouble can unsettle him and impair his performance.
Psycho-emotional instability can be expressed:
- weak;
- moderately;
- strongly.
Affectivity is the so-called emotional impulsiveness: a person reacts violently to any stimulus, it is difficult for him to control himself, and his mood can change to the opposite in a very short time for no apparent reason.
Also, affectivity is approximately the same thing as increased emotional excitability .
Emotional swing is another term closely related to the topic of emotions in psychology. This is the name of a condition in which a person changes his mood and attitude towards certain people in a short time, and this is repeated many times.
Emotional swing is a common method used by manipulators and abusers. They alternate good treatment with bad, inflict pain, and then give compliments and gifts so that the victim does not dare to take any action to save himself.
In such situations, the victim finds himself in an emotional swing : today he hates the abuser, is scared, upset and begins to think about how to get away from him, and the next day he receives a ton of seemingly sincere apologies, compliments, gifts and begins to doubt what he experienced yesterday, and her mental well-being is improving. This contributes to the formation of addiction.
the emotional arousal scale when working with psycho-emotionally unstable patients .
To understand what part of the scale the patient is on, they offer him to undergo tests that reveal the degree of his instability. There are many such tests, but the most famous are the following:
- the “Emotional excitability - stability” technique created by B. N. Smirnov ;
- questionnaire "Scale of temper", developed by Kovaleva P. A. and Ilyin E. P .;
- The “Characteristics of Emotionality” test, focused on self-test, was created by E. P. Ilyin .
Such tests can help not only specialists, but also people who are not familiar with psychology and psychotherapy, since they can help understand how severe instability is and whether it is worth visiting a psychotherapist.
Emotionally unstable personality disorder , which in some sources may be called emotional-volitional instability syndrome , is a type of personality disorder in which one of the key symptoms is the emotional instability of the individual.
Main symptoms of the disorder:
- volitional disorders due to which a person has poor control of himself and his emotions;
- lack of balance, haste in decision making;
- lack of desire to take into account the consequences of decisions made;
- aggressiveness, frequent outbursts of anger.
The first signs of the disease are observed in childhood and the transition period. There are two types of disorder:
- impulsive;
- borderline.
Control of behavior and emotional state is carried out with the help of mood-timing medications and antipsychotic drugs.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of psycho-emotional instability:
- Impaired ability to control emotions. It is extremely difficult for an unstable person to restrain himself during an emotional outburst; he may begin to behave inappropriately.
- Frequent mood swings. At the same time, the severity of the changes is extremely strong: from joy, a feeling of happiness, calmness to palpable depression, accompanied by a desire to cry and be inactive.
- Increased tearfulness, sometimes for no reason. Even a minor nuisance like a burnt breakfast brings tears to your eyes. Also, such people note that they began to react more strongly to sad news, tragic moments from films and books.
- Difficulty concentrating. If every little thing brings you to tears, it can be really difficult to concentrate.
- Irritability, anger. Any disagreement with an opinion or conflict with someone causes a strong emotional reaction: a person can lose his temper, say something rude, or even resort to physical violence. More typical for men.
- Impulsiveness. Decisions are made too hastily and thoughtlessly. This is especially noticeable during short-term “outbursts” (which may contain both an aggressive and a depressive element). A psycho-emotionally unstable person can even commit suicide at such moments.
The set of symptoms can vary and greatly depend on the causes of this condition. If the instability is associated with a mental illness, the above-mentioned symptoms are added to the signs characteristic of such an illness.
Causes
The main causes of the violation:
- an abundance of stress and psycho-emotional shocks;
- hormonal changes in the body;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system (for example, anger, aggressiveness and impulsiveness in men may indicate an excess of testosterone);
- the presence of organic brain damage;
- mental disorders: neuroses, various types of depression, bipolar disorder, manic disorder, personality disorders and many others;
- the influence of some character accentuations;
- chronic overwork, lack of sleep, hunger, malnutrition (including various extreme diets);
- side effects of certain medications and psychotropic substances;
- personal characteristics;
- congenital defects of the nervous system;
- lack of vitamins and minerals;
- some somatic diseases affecting mental health.
What strengthens?
Factors that aggravate psycho-emotional instability:
- stress;
- lack of sleep, malnutrition, hunger, lack of rest;
- psycho-emotional shocks;
- various somatic diseases (deterioration in general well-being may lead to worsening symptoms of the disorder);
- poor quality nutrition;
- lack of treatment for mental illness, if any;
- being in a turbulent, uncomfortable environment, forced communication with unpleasant, toxic people.
Clinical manifestations
ENRL in humans can occur in two variants – borderline and impulsive. The impulsive type is characterized by a violation of one's own self. This leads to uncertainty of intentions and internal preferences. The first signs of the disorder appear in adolescence. These include:
- Frequent fantasizing. Fantasies are of a different nature, often associated with the patient’s family and loved ones.
- Unreasonable change of mood. Emotional lability progresses with the course of the disease.
- A teenager often changes hobbies, for example, clubs and sections he attends.
- Failure to comply with the rules established in the team, disregard for the norms and rules prevailing in school, college, university, friendly company and other social institutions.
- Relationships with others are unstable. The child does not have permanent friends, and he cannot gain a foothold in the team.
- A normal level of intelligence is accompanied by poor performance in educational institutions.
As a patient with a borderline form of emotionally unstable personality disorder grows up, the clinical manifestations change. The following symptoms come to the fore:
- A person tries to do his job as well as possible. Perfectionism can lead to the patient sabotaging his own activities and missing deadlines.
- Emotional reactions are pretentious and exaggerated.
- Self-determination is violated, self-identification suffers. A person has doubts about the chosen educational institution, work or his own personal life. It constantly seems to him that he is making a mistake that can ruin his life.
- Life goals, values, and moral guidelines are constantly changing.
- A craving for psychoactive substances, alcohol, and psychoactive drugs appears.
- It is easy to instill in the patient any ideas by presenting them “with the right sauce.”
- Suicidal tendencies appear.
Patients retain the ability to socially adapt. With a compensated disorder, patients experience a good mood and increased performance. However, dysthymia soon develops. This is a condition characterized by emotional lability and progressive depression.
Emotionally labile personality disorder
Impulsive type . The disorder is rare and occurs predominantly among men.
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA A. The general criteria for a personality disorder must be met B. The presence of at least 3 of the following, and one of them must be 2):
- a pronounced tendency to act unexpectedly, without taking into account the consequences;
- a pronounced tendency to conflict behavior, especially when trying to prevent or influence impulsive actions;
- a tendency to have outbursts of anger or violence with an inability to control the “behavioral outbursts” that result from these emotions;
- difficulty continuing activities that do not offer immediate rewards;
- unstable and capricious mood.
CLINICAL The main feature of the disorder are episodes of loss of control over aggressive impulses. An outbreak of aggression occurs when there is a clearly inadequate reason for such behavior. The period of growth of internal tension to aggressive behavior is several minutes to hours. The attack ends quickly and patients, unlike dissocial personality disorder, regret what happened.
TREATMENT Lithium and carbamazepine are used to control impulsivity. In the case of taking benzodiazepine tranquilizers, a paradoxical increase in impulsivity is possible.
Methods of group and family psychotherapy are aimed at smoothing out the consequences of aggressive behavior.
Borderline type . Borderline personality disorder occurs in 1-2% of the population, and is twice as common in women as in men. The name of the disorder is due to the idea of an intermediate position between neurotic, affective, personality disorders and schizophrenia. There is a hereditary predisposition to this disorder. Up to 70% of people with this disorder were sexually abused as children.
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA A. General criteria for personality disorder must be met. B. At least three criteria B for the impulsive type must be met and additionally two of the following:
- disorder of perception of oneself, one's goals and internal preferences (career, friends, values), including sexual ones;
- a tendency to form intense and unstable relationships that often lead to emotional crises;
- excessive efforts to avoid solitude;
- recurrent threats and acts of self-harm;
- chronic feeling of inner emptiness.
PSYCHOTHERAPY The therapist's ability to tolerate aggressive behavior and maintain the therapeutic relationship is important to the success of psychotherapeutic treatment.
Cognitive therapy allows you to replace mental cliches that divide people into very bad or very good. Behavioral therapy is also used to control impulsivity and outbursts of anger, and social skills training. Cognitive behavioral therapy, including individual and group treatment methods, shows good results.
Encouraging results have been demonstrated using cognitive-analytic therapy and psychodynamic therapy.
DRUG TREATMENT To control impulsivity and unstable mood, lithium, carbamazepine, and antidepressants (fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, MAOIs) can be used.
For anger, hostility and paranoid ideas, small doses of antipsychotics (haloperidol, neuleptil) are used.
Impulsive option
The impulsive type of emotionally unstable personality disorder manifests itself in preschool age. It is manifested by increased emotional excitability and a tendency to engage in various types of actions without assessing their consequences. Children with the disease are aggressive, often raise their voices, and are embittered towards the people around them. They are characterized by the following symptoms:
- children are capricious, easily offended by any words of their parents or peers;
- irritability and cruelty towards people, patients are vindictive and vindictive;
- a gloomy mood and negative emotions prevail;
- the patient tries to be a leader in the team, otherwise he shows aggression;
- tendency to conflict, intransigence;
- study and work do not arouse interest and become uninteresting.
Affective disorders are characteristic of the impulsive type of disorders. They manifest themselves in outbursts of cruelty and aggression. Patients do not think about the consequences of their actions. As a rule, the actions of patients are dangerous for others. People with emotionally unstable personality disorder often experience sexual deviations.
Essence, causes and symptoms of the disorder
Borderline disorder is a disorder of personality self-regulation, especially in the emotional sphere. People with borderline disorder live by pleasure and desire. At the same time, they are not afraid of risks, and real dangers go unnoticed. These people are unstable in interpersonal relationships, self-image and emotions, and impulsive.
Borderline disorder occurs against the background of unfavorable social conditions of development. Because of this, the functionality of the system responsible for regulating emotions is disrupted at the biological level. In turn, the unfavorable environment and existing violations begin to interact and influence each other, further worsening the situation. The result is pronounced dysregulation of the emotional sphere.
Borderline disorder is more common in women, especially those from dysfunctional families. Negative factors include organic damage at an early age, violence at an older age, problematic relationships with parents or lack of care on their part.
People with borderline disorder typically:
- instability of social connections;
- high impulsiveness;
- identification problems.
Additionally, self-harming behavior or threats about it (“If you don’t do what I want (don’t give it to me), then I will kill myself,” “Don’t leave, don’t leave me, I’ll cut my wrists”), and suicide attempts are noted. Aggression can transfer to others if the patient feels that they are encroaching on his values.
Borderline individuals are convinced that their parents did not love them, and therefore the former have every right to be offended by them and demand attention from other people. Therefore, people with borderline disorder regularly seek help, care and concern, but at the same time they are hypersensitive to rejection or loss. When they feel cared for and find the next victim of relationship drama, they exaggerate one side of themselves that needs help: depression, addiction, eating disorders, somatic complaints and whims about not being cared for enough. When the caregiver gets fed up and leaves, the borderline personality exhibits a second side: intense and inappropriate anger.
These “swings” are accompanied by the same changes in attitude towards oneself, the world, and other people. Perception constantly fluctuates between “good - bad”, “love - hate”, etc.
As for the “caregivers,” at first they begin to give care with pleasure and sincerely, but gradually (as crises, inadequate demands and complaints increase) they get bored. And they respond in kind to the hostility of a person with a disorder.
Borderline disorder is often aggravated by addictions (alcohol, drugs) and sexual promiscuity. Without correction of the condition, somatoform disorders and psychoses develop.
Complications of the disease
In the absence of therapy, as well as when attempting self-treatment, ENRL can lead to negative consequences. Patients often develop chemical dependencies - alcoholism and drug use. These habits lead to rapid progression of disorders and a sharp increase in symptoms. As a result, organic disorders develop in the nervous system and internal organs.
Long-term personality disorder can cause depression. Such disorders tend to progress and gradually lead to a decrease in the patient’s quality of life. Their treatment requires the prescription of antidepressants. Patients with emotionally unstable personality disorders pose a threat to themselves and the people around them.
To prevent complications, it is recommended to always seek professional help from a doctor. You can call a psychiatrist at home or attend a consultation directly at the clinic. The specialist is able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy.
Diagnosis of emotionally unstable personality disorder
Detection of ENRL requires a comprehensive examination by a psychiatrist. The specialist talks with the person, finds out information about his education, work experience and communication with other people. In case of emotionally unstable personality disorder, it is recommended to have a conversation with the patient’s relatives or friends. Patients themselves may deny any disorders. Often they are cunning, trying to hide the true picture of what is happening.
To make a diagnosis, the patient must have at least 5 symptoms from this list:
- Violations of self-determination. The patient does not have a stable image of his own “I”. The image of one’s own personality is blurred, the details in it do not fit together well.
- A person avoids loneliness. He makes excessive efforts, often thoughtless actions, to attract attention to himself.
- The presence of unstable and tense close relationships, which are accompanied by idealization or devaluation of the other person.
- Psychological impulsiveness in any two areas of a person’s life: thoughtless use of money borrowed, alcoholism and other extremes.
- Emotional instability, imbalance.
- Suicidal behavior, including hints and threats to the act of suicide, its preparation, and the implementation of plans.
- Constant feeling of emptiness, weakness, loss of strength.
- Paranoid ideas or symptoms of personality dissociation.
- Affective disturbances with sudden outbursts of anger and rage.
To exclude brain damage, patients undergo electroencephalography. This method evaluates the electrical activity of individual structures of the central nervous system and makes it possible to easily identify their damage. If tumors, encephalitis or other organic disorders are suspected, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is performed. The examination results are interpreted only by the attending physician.
Treatment of emotionally unstable personality disorder in Moscow
The treatment of the disorder is chosen by a psychiatrist based on medical history and information about the examination. The therapeutic process is controlled by the person’s relatives, since patients independently abandon taking medications and visiting a psychotherapist. The person does not need to be hospitalized. He can be treated at home.
During sessions, the doctor identifies a person’s thoughts that push him to impulsive statements and actions. Once they are discovered, ways to avoid, bypass or replace them are suggested. Long-term cognitive behavioral therapy can achieve a positive effect in most patients.
In the process of treatment for emotionally unstable personality disorder in Moscow, the patient keeps an individual diary. It allows you to systematize work on sensations. The specialist divides the psychotherapeutic session into three stages:
- discussion of behavior and actions that pose a threat to the life of a person and those around him;
- conversation about behavior that leads to a decrease in quality of life and a decrease in the effectiveness of psychotherapy;
- teaching constructive behavior patterns.
The last stage is consolidated in group sessions, which last up to 1.5-2 hours. Use role-playing games and special exercises. After classes, all patients with ENRL are given homework. Cognitive behavioral therapy is considered the most suitable method for eliminating signs of emotionally unstable personality disorder. The method is suitable for most patients and has no contraindications. The only drawback of the approach is the duration of psychotherapy, which can reach several years.
For severe dysthymia accompanied by depression, the doctor selects antidepressants. Preference is given to drugs from the group of selective serotonin reuptake blockers. They are well tolerated by patients and rarely lead to side effects. In addition to them, other groups of drugs can be used: anticonvulsants (Phenobarbital, etc.), lithium salts. They have an anti-anxiety effect and normalize the emotional background of the patient.
With severe affective disorders and hyperexcitability, the patient may be prescribed antipsychotics. For example, Risperidone or Phenazepam. They normalize the patient’s behavior and allow him to avoid aggression towards himself and the people around him.
Additional positive effects can be achieved through meditation and relaxation techniques. With regular meditation practices, the overall level of stress decreases and awareness of actions increases. This has a positive effect on a person’s well-being and has a beneficial effect on his relationships with other people.
Treatment
Treatment must be supervised by loved ones, since individuals with borderline disorder tend to leave therapy as soon as they feel better. They return again when there is a natural deterioration. Obviously, such treatment will not produce results.
People with borderline disorder need regular motivation and support, empathy. The name of the disorder speaks for itself - patients are constantly on the brink of feelings, emotions, decisions, and so on, moving first to one side, then to the other. By doing this, they drive everyone around them, and sometimes even their treating doctors, into a state of frustration.
People with borderline disorder are very difficult to help. The most effective means for correcting the condition today is dialectical behavior therapy by Marsh Linech. Therapy includes the following components:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy. The goal is to teach the patient self-control and the “here and now” principle.
- Dialectical approach. It involves working with cause-and-effect relationships, namely eliminating boundaries and changing the thinking “as I did, so it will be” to “either this, or this will be the case.” Truth is formed cumulatively, including on the basis of contradictions. It is useless to reason logically or have a calm conversation with a person suffering from a borderline state.
- The principle of harmony. Various meditation and relaxation techniques are necessary to understand the unity of the world and the connection of all its parts, including opposite ones. A person must realize and accept himself and his experience, establish connections between the past and the present. The very basis of relaxation is contradictory - to accept, but at the same time to detach, and sometimes to change due to acceptance. For example, you need to accept psychological trauma for the sake of your own changes.
- Metaphors. During therapy, it is important to keep the patient active and stimulate him to move. This is done using healthy humor, metaphors and the principle that "patients may not have created all their problems, but they must solve them one way or another."
The author described the subtleties of therapy, principles, technology, and even the metaphors themselves in his book “Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Borderline Personality Disorder.” Therapy lasts at least a year and is performed on an outpatient basis. The main elements of treatment include individual and group psychotherapy. Sometimes drug therapy or hospitalization is used when the patient is in crisis.
During individual sessions, the patient fills out a diary. Sessions are built in a certain sequence:
- life-threatening behavior is discussed first;
- then – behavior that interferes with psychotherapy and reduces the quality of life;
- Afterwards, the patient learns constructive behavior skills.
Skill training and practice continues in group classes, which last longer. Exercises and role-playing games are used, and homework is given. The group therapy program and didactic material are also presented in the author's manual. Group classes are divided into blocks: emotional regulation, increasing stress resistance and developing adequate reactions to traumatic events, increasing the effectiveness of interpersonal relationships, developing the ability to understand the unity of the world and one’s involvement in it.
The method of dialectical cognitive behavioral therapy requires a lot of time and money, and also places severe demands on the professionalism of the specialist. But so far this is the most effective method of correcting borderline disorder. It is impossible to independently help a person with a disorder with socialization.
Disease prevention
There is no specific way to prevent emotionally unstable personality disorder. This is due to the fact that the specific cause of the pathology has not been established. Prevention of the disease is divided into primary and secondary. Primary prevention is carried out in healthy people who have risk factors for developing the disease.
This includes the following actions:
- Avoiding physical punishment of the child.
- The family must maintain positive, trusting relationships. Any aggression and cruelty are completely excluded.
- When communicating with a child, it is necessary to support his independence and help him identify his own “I”.
Secondary prevention is carried out for patients diagnosed with emotionally unstable personality disorder. It allows you to prevent the progression of pathology and the development of complications. To do this, a person must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Reduce stress levels in life. To do this, it is recommended to eliminate stressful situations and meditate regularly.
- Eliminate bad habits, primarily alcoholism and drug use.
- Follow doctor's orders.
- Change jobs if there is excessive workload and a toxic team.
If you experience any symptoms of a personal disorder, you should immediately contact a psychiatrist. The specialist will conduct an examination and promptly select comprehensive treatment.